This workstream covered topics related to maintaining distribution system reliability from the distribution utility perspective. These topics included distribution planning mechanisms to ensure reliable participation of DERs in aggregations, and reliability override of operational dispatch if needed to ensure distribution system reliability. The primary driver behind the workstream was the definition of DERs in FERC Order 2222, which pertains specifically to resources interconnected to the distribution system, thus underscoring the critical role of distribution utilities towards maintaining the reliability of the distribution system and ensuring that ISO/RTOs meet the compliance requirements.
The first task of the workstream was to outline the roles and functions of distribution utilities as required by Order 2222 in three distinct timeframes: intercon¬nection, DER aggregation review, and ongoing operational coordination. Several introductory frameworks for addressing new and evolving functions were introduced, with the intent of leveraging existing and emerging technology, processes, data, and tools. The overarching goal was to summarize the Order’s requirements for distribution utilities and the implications across the key areas impacted.
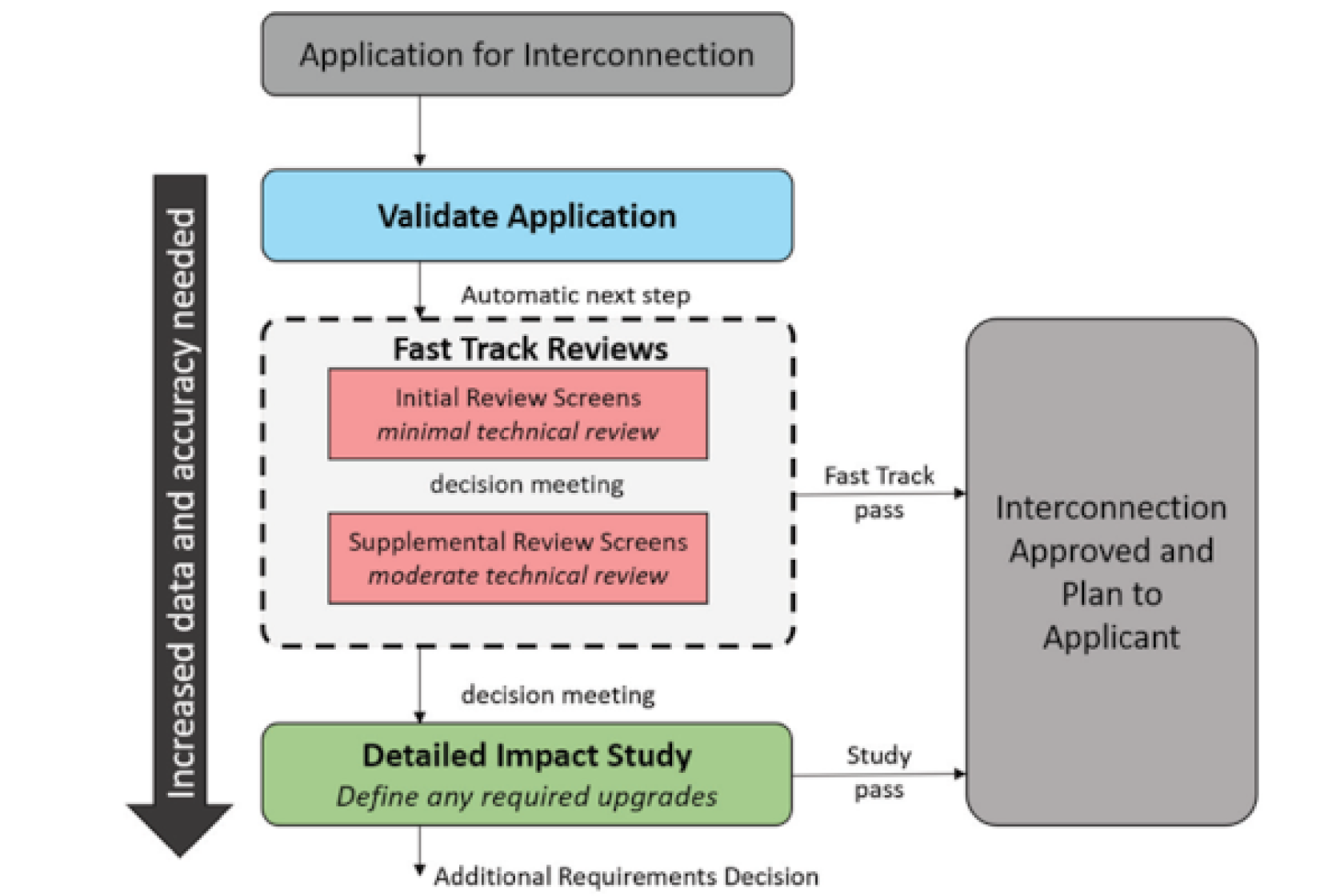
DER interconnection review process used by utilities.
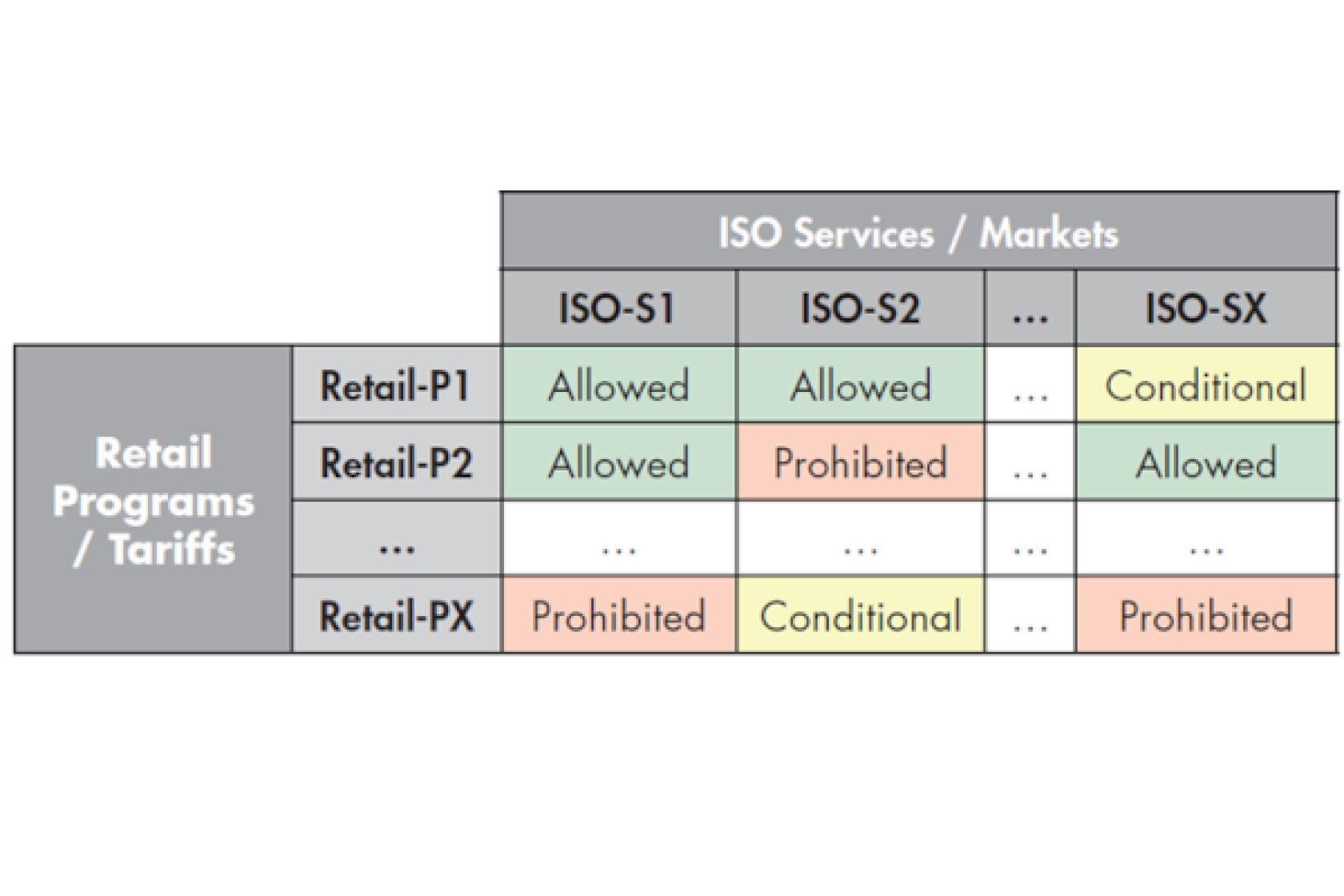
Reconciliation of retail and wholesale programs or tariffs that are available for DERs to participate in, both individually and simultaneously, is vital, and can be accomplished via ‘DER Program Compatibility Matrix’.
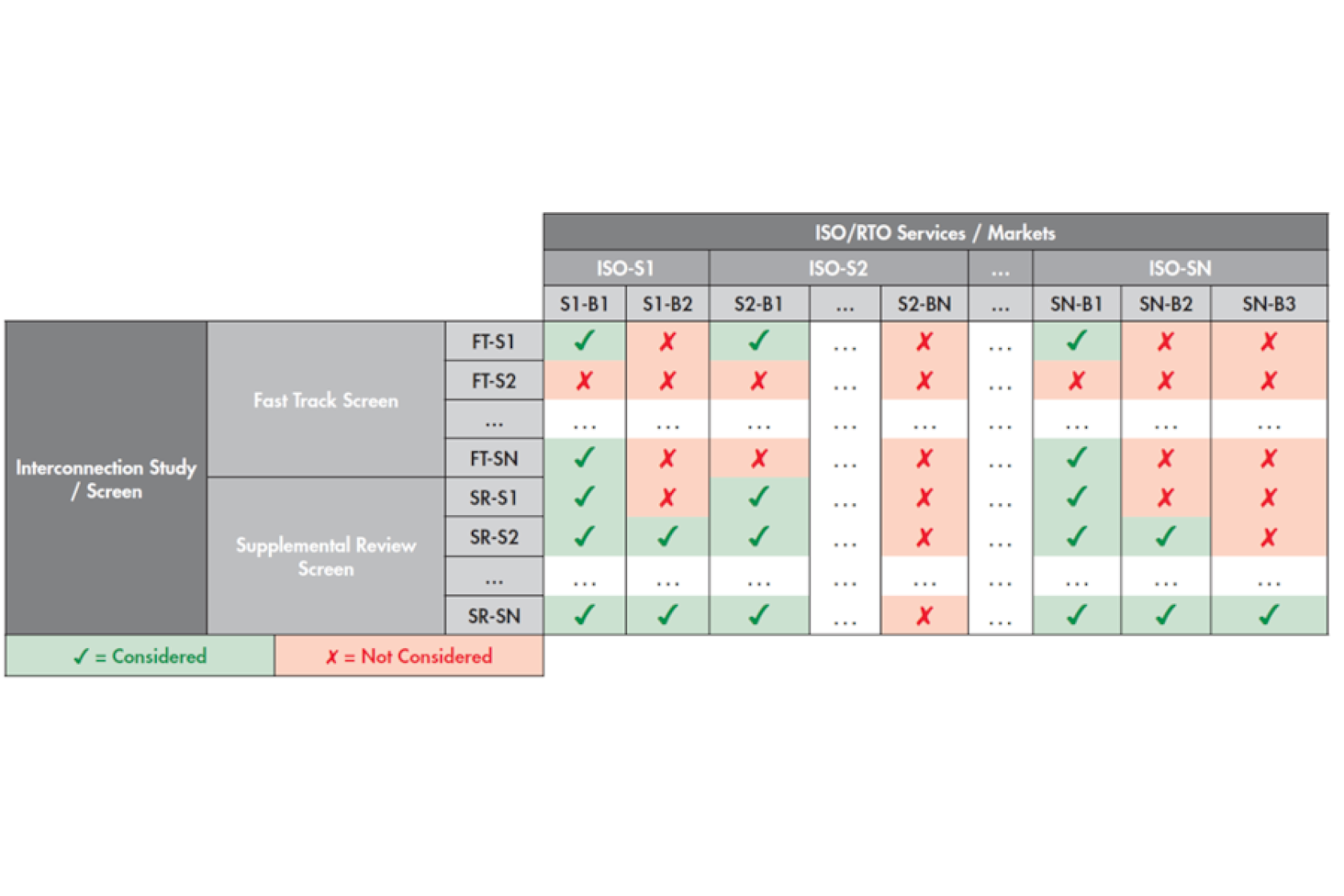
DER Services Impact Matrix’ helps capture the impact of DERA market participation.
The second task for this workstream addressed the technical and procedural challenges that distribution utilities face in implementing Order 2222. It described the current state of distribution planning and operational analytical capabilities, and their suitability for meeting the needs of the Order. Through this task, interconnection studies and operational tools were determined to be the highest priority for modifications. Moreover, currently emerging tools were identified as potentially necessary for maximizing DER availability and minimizing disruptive curtailments.
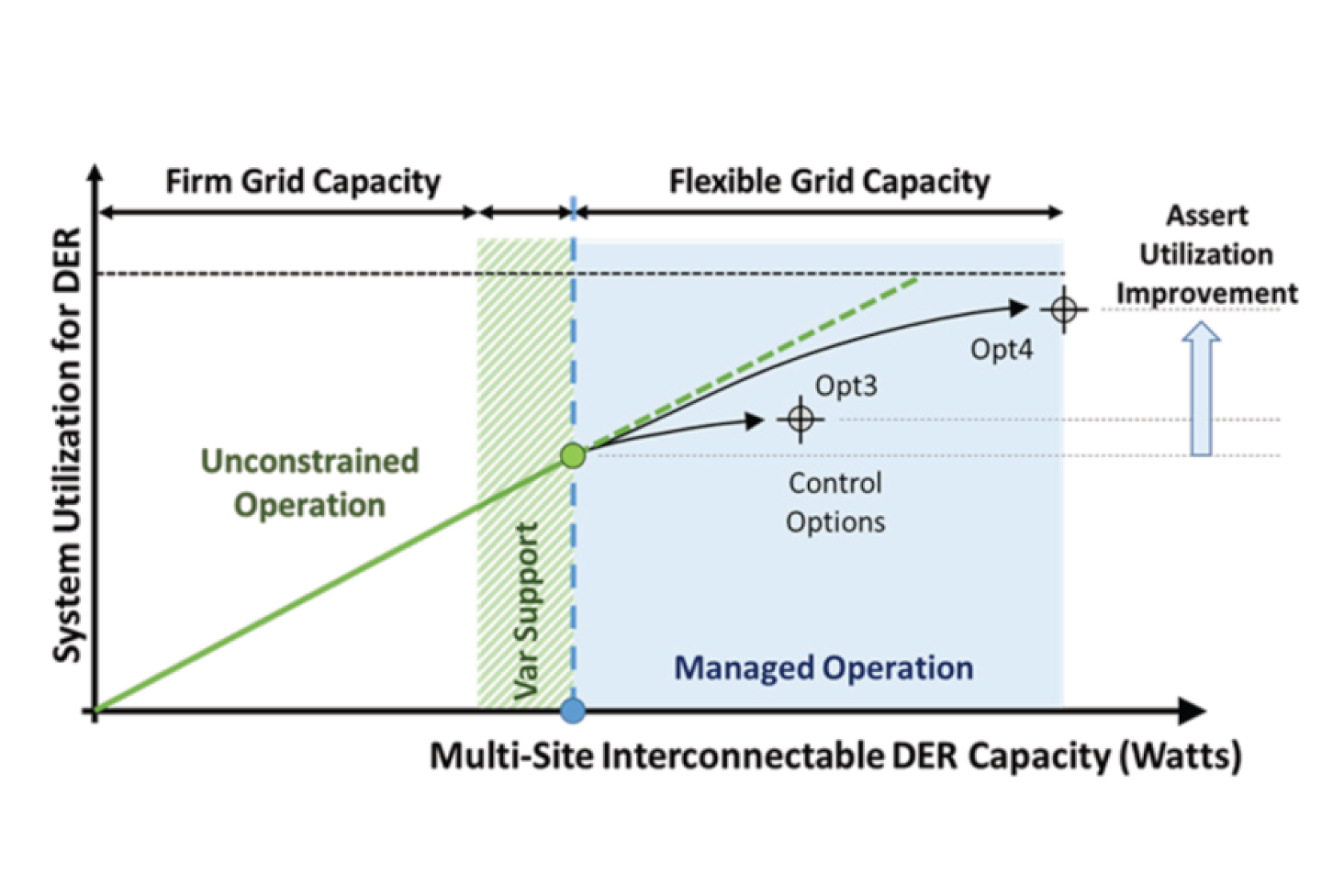
Flexible Interconnection Capacity Solutions allow utilizing the hosting capacity based on changing constraints.
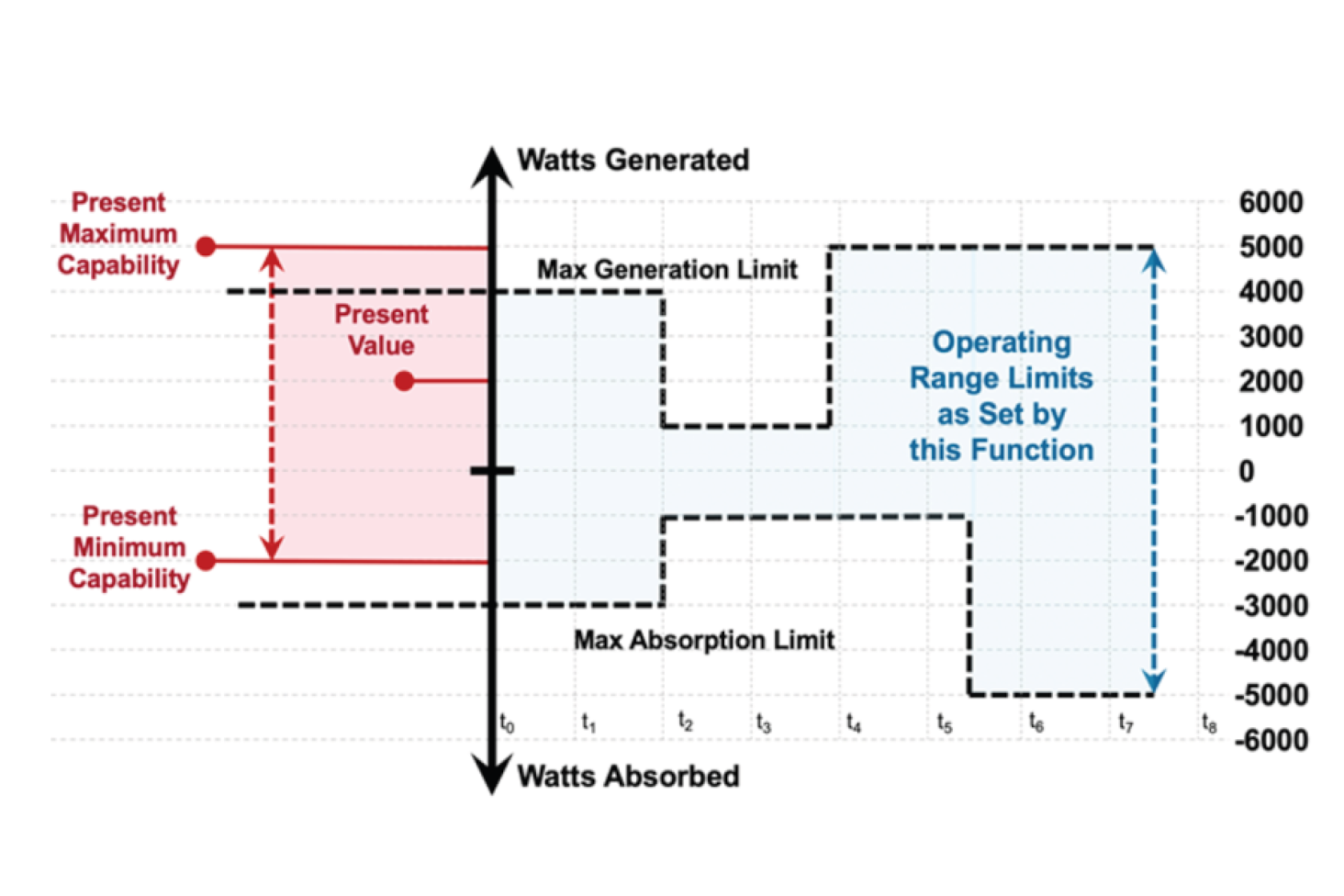
Operating envelopes provide capacity allocation projections which can be used for planning and managing DERA dispatch.
Key Takeaways
-
To capture the impact of DER aggregation market participation during the interconnection study process, a practical first step for distribution utilities is to work with ISO/RTOs to document and standardize the performance requirements for various wholesale services.
-
Utilities can take the first step to review interconnection study practices in an effort to understand how well studies and screens during the interconnection process capture aggregated market participation.
-
Distribution utilities, ISOs/RTOs, and RERRAs must agree upon the compatibility of existing retail programs with the available wholesale services or products.
-
Under a flexible interconnection paradigm, larger plant sizes might be permissible at more locations through managed operation of the DER’s active and reactive power.
-
The creation and communication of operating envelopes to assist in planning and managing the dispatch of DER aggregations should be investigated.