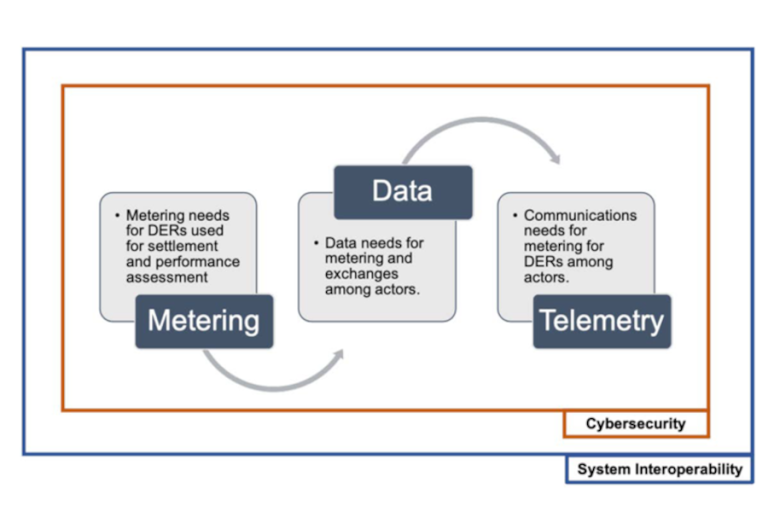
This workstream covered topics related to secure communication and information exchange to meet the evolving needs of DER aggregation participation in wholesale markets. The primary audience is ISO/RTOs, transmission operators, electric utilities, and DER aggregators. In addition, the recommendations could be relevant for state and federal regulators and DER customers (owners and operators of DERs). In terms of the scope, the workstream specifically provided assessments on five core areas: metering, telemetry, data information sharing, system interoperability and cyber security. The first three core areas have direct relevancy to Order 2222, whereas the remaining two are cut across the first three core areas.
The five core areas are defined as:
-
Metering is the measurement of energy, either consumed or produced, used for settlements.
-
Telemetry is the ISO/RTO process(es) for direct measurement and communication of requisite physical, operational, and performance characteristics of a DER.
-
Data is the information related to DERs, actors, settlements, and performance monitoring of individual DERs.
-
Interoperability is the ability of the DER systems to exchange requisite data and information among the relevant smart grid domains and actors, markets, and networks.
-
Cyber security includes maintaining the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of requisite data and DER systems.
FERC Order 2222 creates a complex coordination equation between DERAs, distribution utilities, ISO/RTOs, and DERs, each with its own communication interface, data requirements, and protocols. The goal of the workstream was to consider the interactions between all the different stakeholders in a streamlined manner and provide better visibility into the DER operations. It highlighted the key considerations and gaps for the five core areas. The existing metering and telemetry infrastructure and data sharing approaches were reviewed extensively, along with the recent promising developments. In addition, different communication, data, and interoperability protocols were discussed. Importantly, the security vulnerabilities associated with the utilization and exchange of data were presented as well as their potential solutions.
| Message | Example Standards |
|---|---|
| Resource registration | IEC 62325-452 |
| Group definition | IEC 61968-5 |
| Market bidding | IEC 62325-452 |
| Market awards | IEC 62325-452 |
| Market schedule | IEC 62325-452 |
| Resource dispatch | DNP3/IEC 61850 |
| Resource interval meter data | (NAESB) REQ 21—ESPI |
Market message exchange standards.
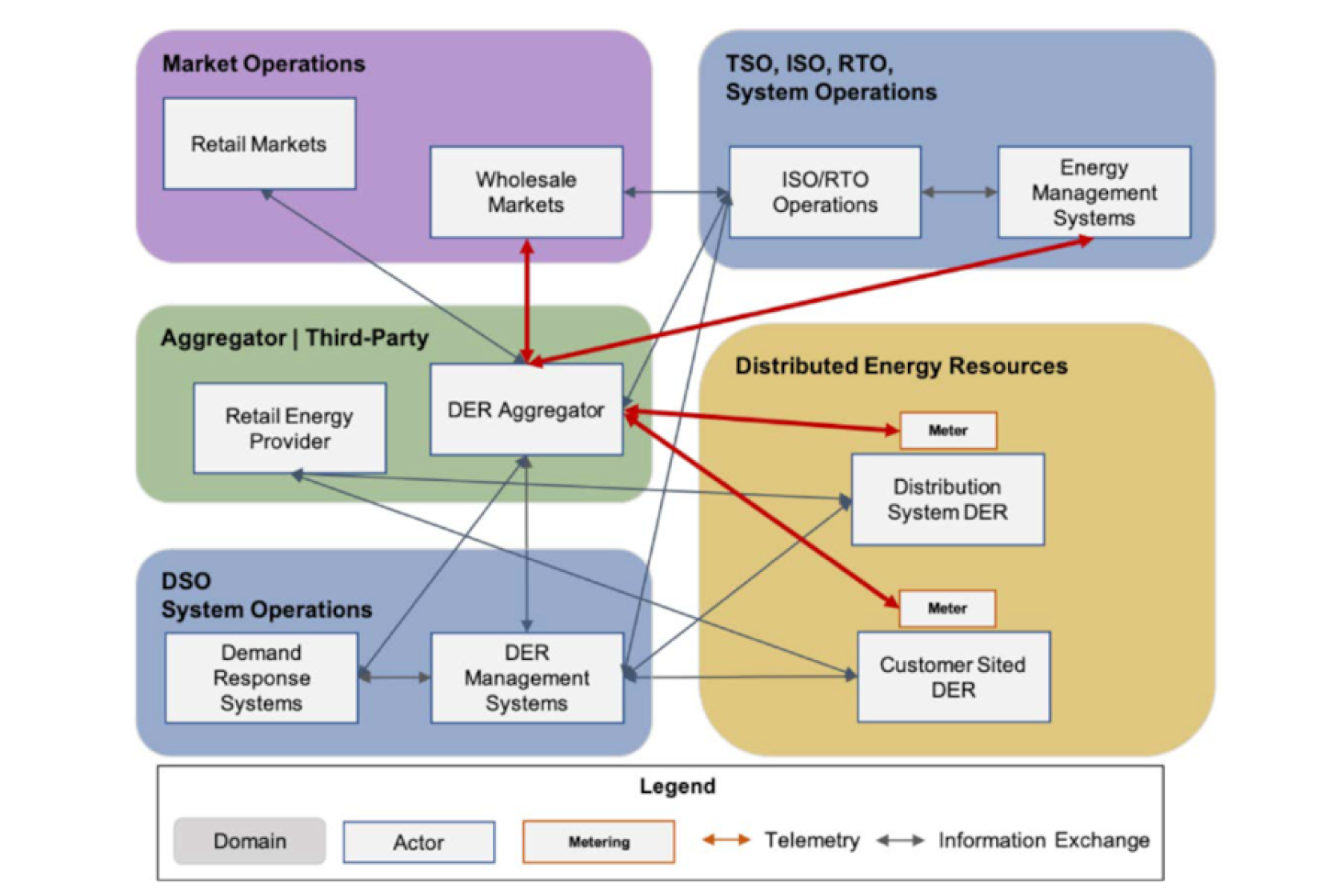
Reference communications architecture.
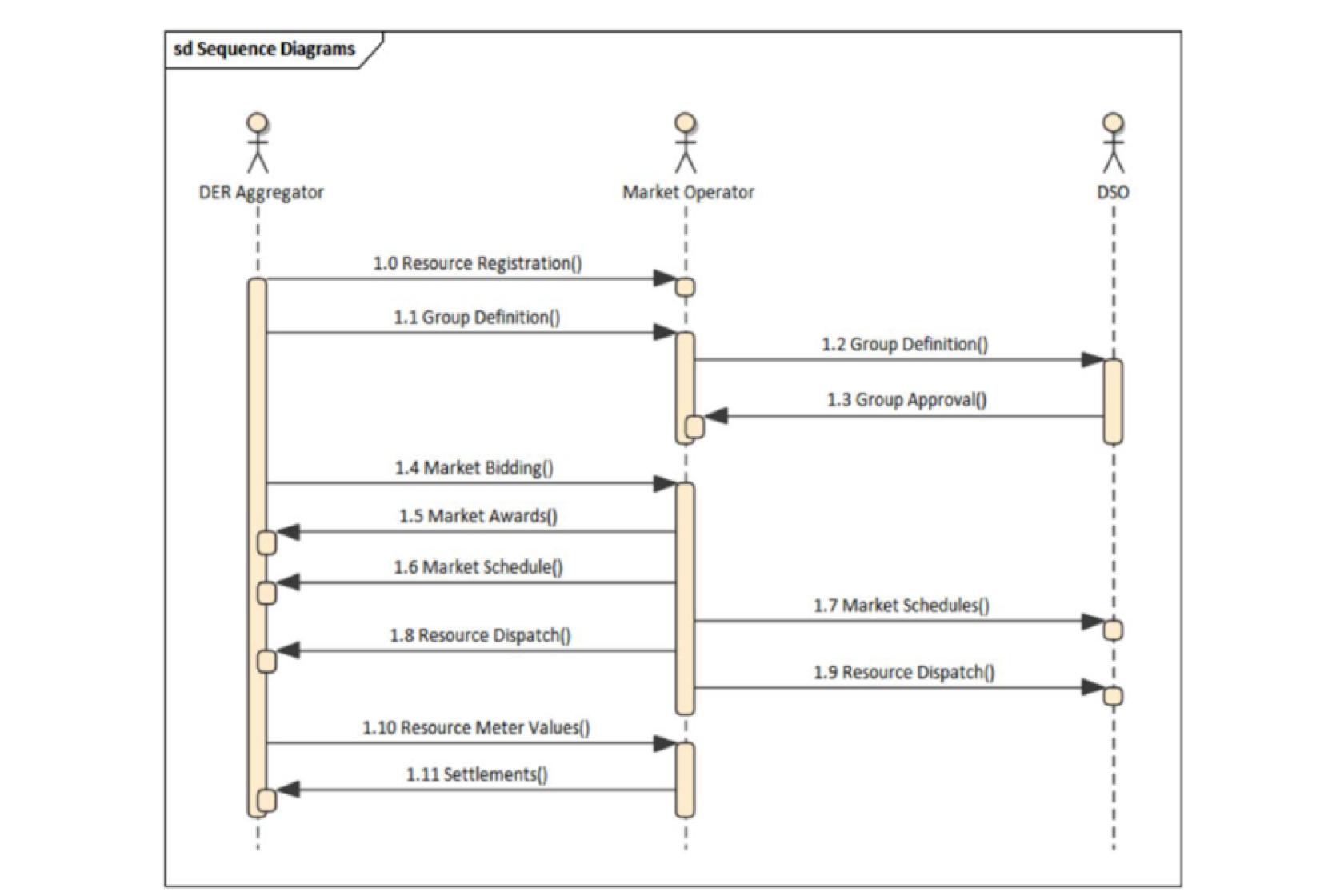
An example sequence of message exchanges in one of the collaboration models discussed in the workstream.
| Source | Target | Message | Contents |
|---|---|---|---|
| DER aggregator | Market operator | Resource registration |
|
| DER aggregator | Market operator | DER group definition |
|
| Market operator | DSO | DER group definition |
|
| DER aggregator | Market operator | Bidding |
|
| Market operator | DER aggregator | Market awards |
|
| Market operator | DER aggregator | Resource schedule |
|
| Market operator | DSO | Resource schedule |
|
| Market operator | DER aggregator | Market dispatch |
|
| DER aggregator | Market operator | Telemetry |
|
| DER aggregator | Market operator | Energy |
|
| Market operator | DSO | Energy |
|
| Market operator | DER aggregator | Settlements |
|
DER market participation exchanges.
Key Takeaways
- Metering requirements may be different for different types of DER.
- Telemetry and the cost of telemetry will play a critical role for DER participation in ISO/RTO markets. Therefore, ISO/RTOs must have clear telemetry requirements and guidelines that align with planning and operational needs, consider cost to DERAs, and align with rules for similar services.
- When interoperability is low, resource integration costs tend to be high. The key to lower costs is standardization.
- EPRI maintains a running list of DER information and protocol standards through the Information and Communication Technologies program.
- The North American Energy Standards Board (NAESB) Energy Services Provider Interface (ESPI) standardizes the business practices necessary for customers to share their meter data.
- Additional research is required to determine an approach that could help standardize the common market interactions for aggregators, consistent with other resource types, without unnecessarily burdening the ISO/RTOs.
- Additional research is needed to develop a scalable architecture to meet the needs of Order 2222 and to update relevant information and protocol standards to support the architecture.
- Interfacing grid entities must establish their own security protocols, as Order 2222 does not specify requirements. Establishing mutual consensus on technologies, procedures, and security language within contractual agreements between grid parties is expected to be a major challenge.
- A chain-of-trust framework will be required to inform the proper security protocols to be coordinated across a multi-party grid.