The workstream covered topics related to maintaining transmission system reliability from the transmission owner or ISO/RTO perspective, including transmission operations tools and transmission planning assessments with active DERs.
The first task of the workstream was to support transmission operators through structured analysis to identify the main issues faced in operations with high DER market participation. The task reviewed the main functions carried out by transmission operators in real time operations and operations planning, identified how DER market participation could influence bulk system opera¬tions, and cataloged several options to integrate DER or mitigate adverse impacts for transmission operators. Overall, it represented a highly structured approach towards assessing the impact of DER aggregations.
Transmission Operations
Real-Time Operations
Maintain situational awareness of the bulk power system
Contingency Analysis
Restoration and Emergency Operations
Congestion Management on Sub-Transmission
Management of System Voltages
Asset Monitoring
Operational Planning
Outage Coordination
Network Model Building & Exchange
Contingency Definition
Functional roles in transmission operations that will be impacted by DER aggregation participation in markets
Functional Role #6: Asset Monitoring
Current Process Summary
Asset managers at transmission owners and operations make decisions on a rolling basis relating to the availability of a transmission asset. Asset managers may schedule maintenance for a given asset based on the asset management policy for the company and may derate or remove an asset from service based on observations from sensors on the device in case of anomalous readings. These considerations apply primarily to transmission owners.
Current Interactions
RTO/ISO
✓
Distribution Utility
✓
DER Aggregator
X
Implications of DER Market Participation
DER growth may substantially change the way assets are used (for example, generators, shunts, or breakers) so that traditional maintenance practices may require revision to ensure that availability of the asset is sustained over the longer run.
Magnitude
The incremental impact of market controlled DER on transmission asset loading and operation may reduce asset loadings on average, but materially increase incidence of changes in the direction of flow through an asset.
Frequency
While the effect of DER on asset utilization is continuous, a material impact may be concentrated to certain locations.

Mitigation Options
Integrate forecasted DER market behavior in asset management assessment tools.
How big a change in process is this mitigation?
TO function for maintaining availability is separate for market forces.
Maintenance and operation are not dictated by the market. Reduce mitigation associated with devices not being used. Try to reduce impact but not forego maintenance.
Examples where this mitigation has been applied
No specific implementation for asset management.
Functional Analysis was performed across different characteristics including Current Process Summary, Current Interactions, Implications of DER Market Participation and Mitigation Options.
The second task in the workstream reviewed several key aspects of transmission planning considerations for wholesale DER aggregation market participation, including long-term planning studies, steady-state and dynamic modeling, screening practices and interoperability requirements. Furthermore, it addressed the need for DER aggregators, Relevant Electric Retail Rate Authorities (RERRAs), and distribution utilities to provide relevant information to RTO/ISOs for performing transmission impact studies, and underscored the role of ISO/RTOs in establishing coordination frameworks and enabling data exchange. Overall, the task discussed pros and cons of different approaches, highlighted outstanding challenges, and proposed potential frameworks to help address these gaps.
Transmission Planning
Reliability Assessment
DER Capabilities, Performance and Functional Settings
Key Data Needs, Exchange and Management
DER Modeling in long-term studies
Analysis for steady-state dynamic stability and bulk system voltage and performance
Technical review and screening
Technical connection and interoperability requirements
Coordination of DER technical settings
NERC Guidelines
Common file format, DER Settings database, and remote configurability
Key aspects of transmission planning that will be impacted by DER aggregation participation in markets
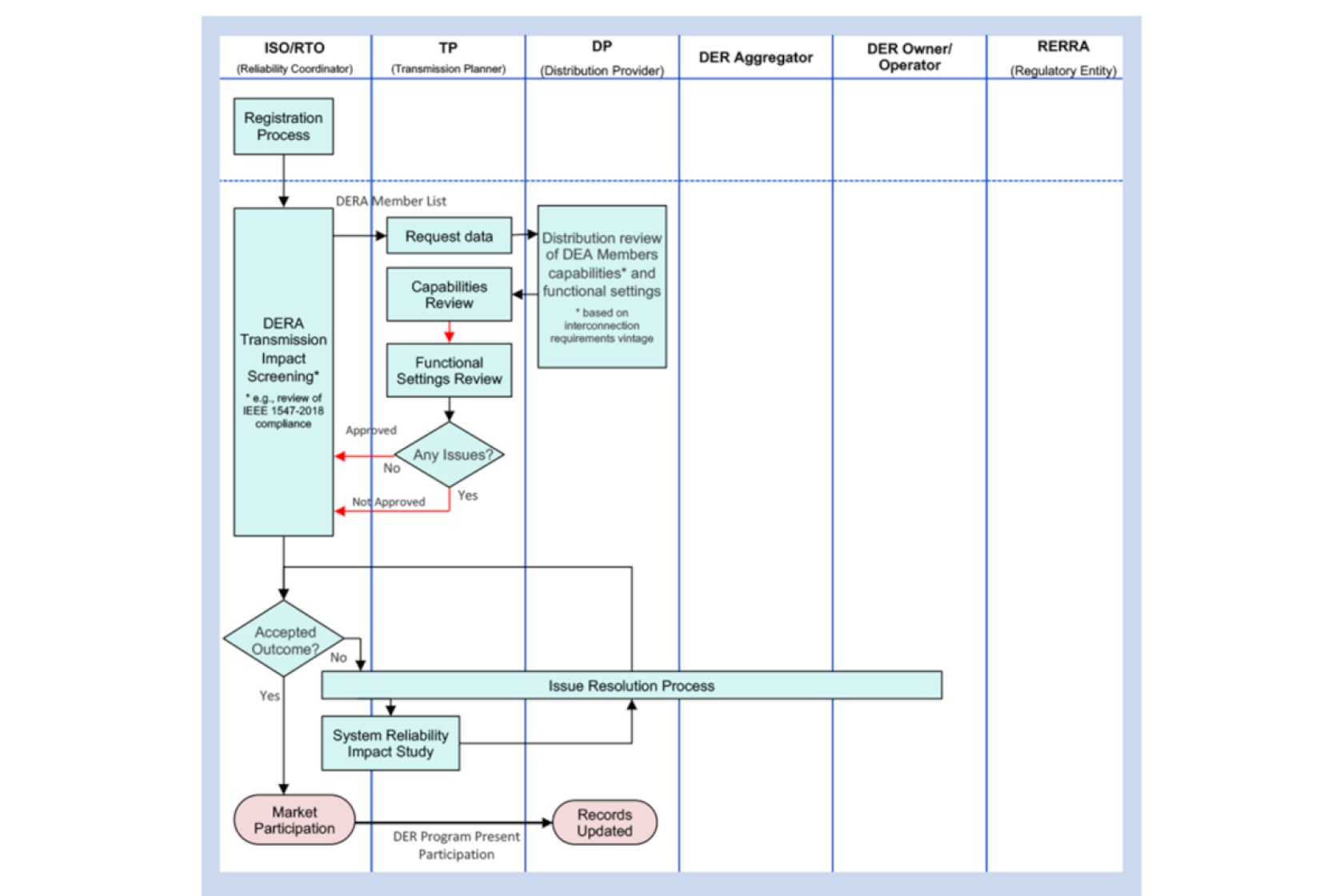
Example DERA Technical Review Process using Screening Criteria used for ensuring system reliability.
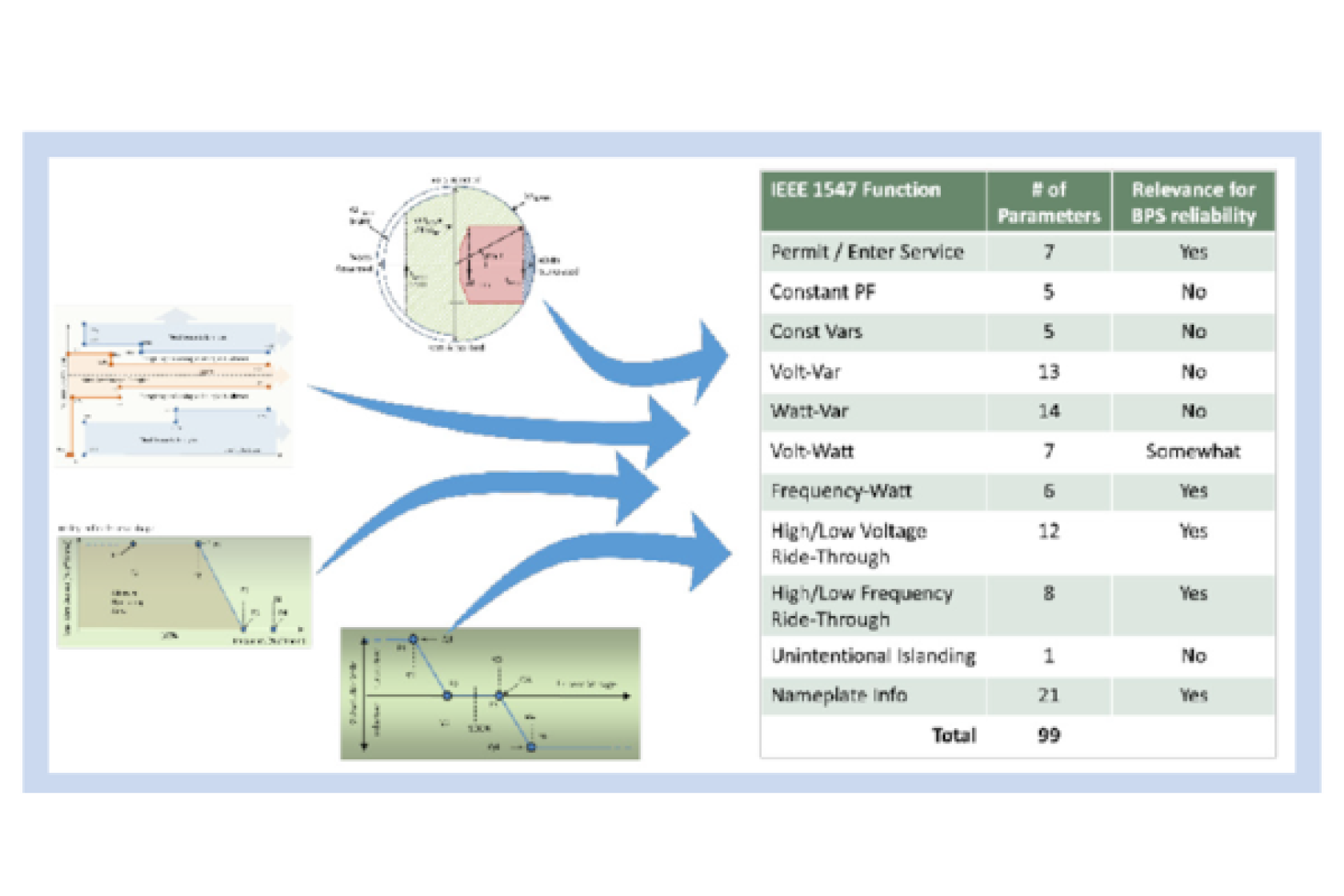
Functional Settings for DERs as standardized by IEEE 1547-2018 to improve interoperability.
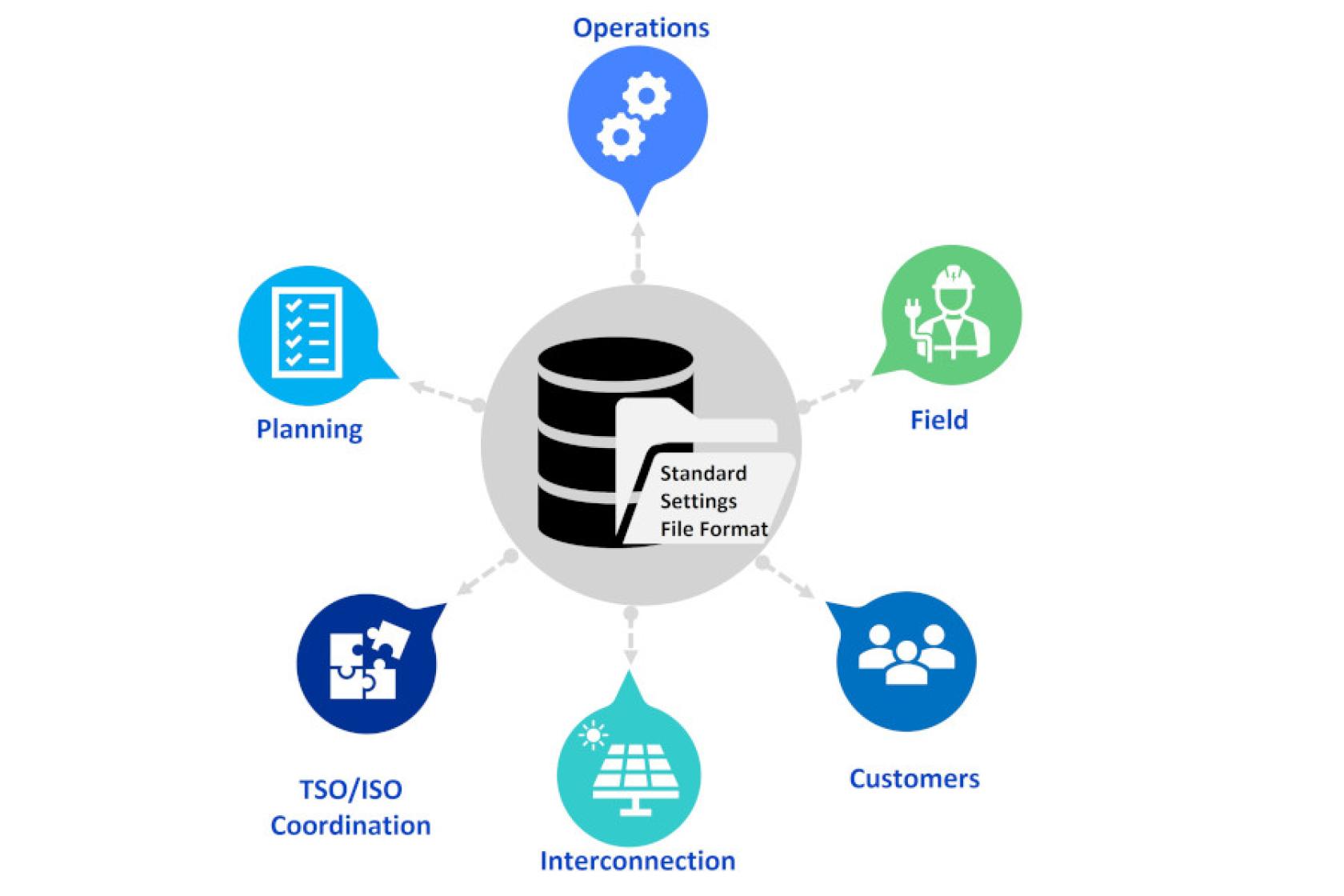
DER Performance and Settings Database with Possible Use Cases for DER Settings Files that Use a Common File Format.
Key Takeaways
Operations
- Cross-entity data exchange is critical to sustaining situational awareness of the transmission system.
- Defining an observability region that extends beyond the network controlled by an individual entity and encompassing assets whose status has a material impact on the operation of a transmission operator’s grid supports enhanced situational awareness.
- Direct telemetry from distribution-connected, utility-scale DER and DER aggregation at a nodal level substantially supports several transmission operator functions.
- Managing abnormal local or system operating conditions requires enhanced coordination and extensive data exchange during emergencies and restoration.
- To facilitate and leverage DERA during periods of grid maintenance, network topology data exchange and outage coordination activities must be enhanced between ISO/RTOs, transmission owners, and distribution utilities.
- DER will cause the lumped dynamic model of the distribution grid to change substantially for short circuit and transient stability analysis.
Planning
- DERA technical review using screen criteria is a simplified process which is effectively complemented by DER transmission impact studies that are already conducted.
- Advanced DER and DERA modeling improvements and parameterization can enable more granular and sophisticated studies where needed.
- Standards such as IEEE 1547a-2020 can be adopted to act as broadly accepted industry reference and for good utility practice.
- The timely establishment of coordination frameworks for DER Functional Settings could be a critical success factor for DERA wholesale market participation.
- The use of EPRI’s common file format can aid the management of DER Functional Settings.