Project Description
In Johor Bahru, Malaysia, a joint venture developing a petrochemical and power generation site using Cogen Technologies needed to build a transmission line connection to the Peninsular Malaysia Grid. Tenaga Nasional Berhad and Petronas required a double-circuit, 275-kV line of 50 km in length to serve as the interconnection (Figure 40). The capacity requirement was 2151 amps per circuit.
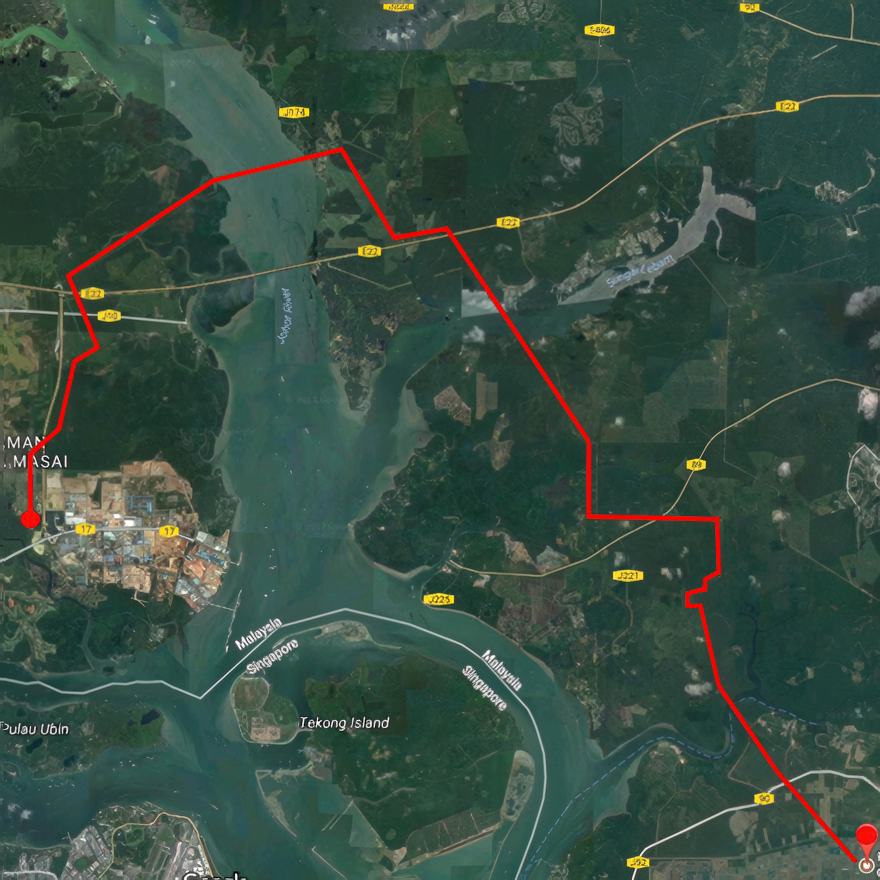
Figure 40. A 50-km line route for the Malaysia Cogen connection
Options Considered
Traditionally, the 275-kV construction used a triple-bundle ACSR Zebra conductor. The project sponsors considered expanding their conductor considerations to allow for increased capacity above initial project requirements, minimizing line losses with high power factor loading and optimizing lifetime costs. The ACCC conductor was given consideration for its increased power capacity for equivalent-sized conductors.
Figure 41 provides a comparison of the solution packages investigated for the project. There were two twin-bundle and two triple-bundle options compared using ACSR and ACCC for each configuration. The twin-bundle ACSR did not meet the required capacity limits and was eliminated.
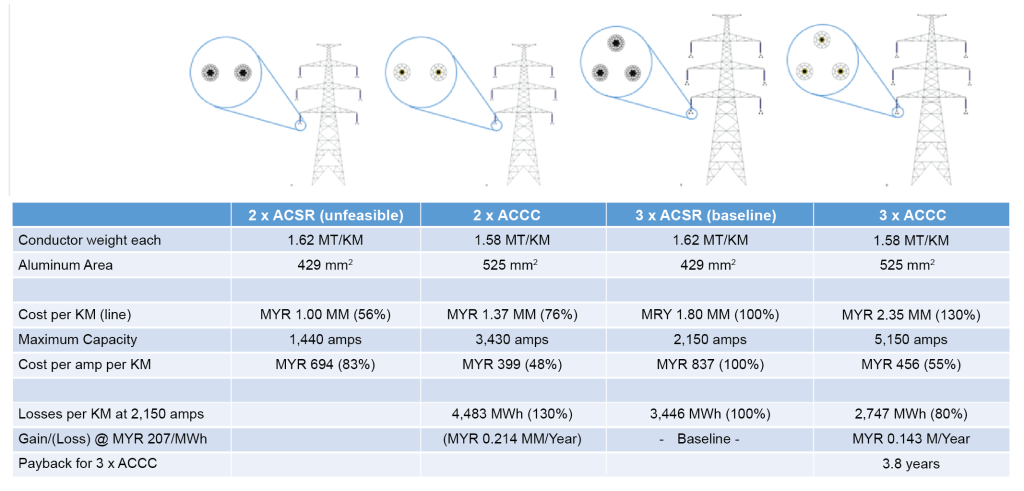
Figure 41. Conductor selection options table
Justification for HTLS Selection
As Figure 41 illustrates, the twin-bundle ACCC option met the capacity requirement and had the lower cost per amp per km value. But the triple-bundle Dublin ACCC option with its increased capacity and modest increase in cost over the twin-bundle option was a clear winner when line losses were incorporated in the evaluation.
Installation Review
Line construction was completed in mid-2017. The line was constructed on a combination of double-circuit steel lattice structures and single steel pole configurations. Figure 42 shows multiple steel pole structures used for the river crossing. Figure 43 shows line workers working on the dead-end assemblies on one of the river-crossing structures.

Figure 42. River crossing—double-circuit, 275-kV line
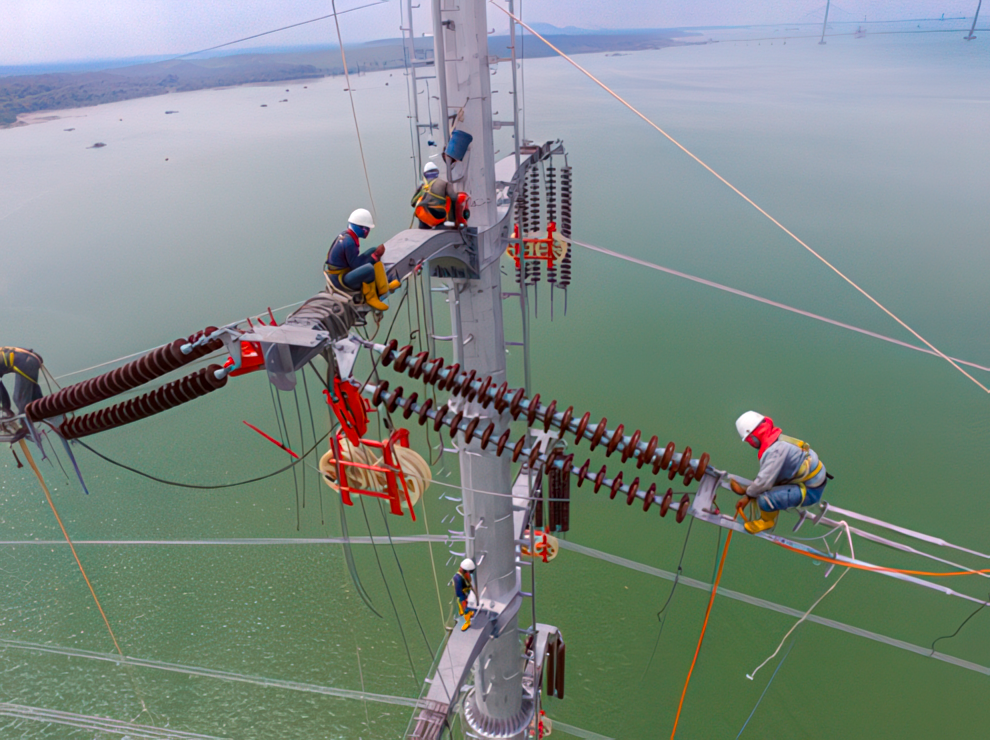

Figure 43. Mid-river dead-end assembly installation